Take away message
- Dilated convolution operator, which can expend the receptive field without losing resolution or coverage, is very suitable for dense prediction task.
- multi-scale context module, can reliably increases accuracy when plugged into existing semantic segmentation systems.
- Replace pooling layer (designed for classification task) with dilated convolution (designed for segmentation task) can increase accuracy.
Model
- dilated convolutions
- $l$-dilated convolution: The familiar discrete convolution is simply the 1-dilated convolution.

use $∗_l$ to represent an $l$-dilated convolution - Let $F_0, F_1, \cdots , F_{n−1} : Z^2 \rightarrow R$ be discrete functions and let $k_0, k_1, \cdots, k_{n−2} : Ω_1 \rightarrow R$ ($Ω_r = [−r, r]^2 ∩ Z^2$) be discrete 3×3 filter. Consider applying the filters with exponentially increasing dilation:
\(F_{i+1} = F_i ∗_{2^i}k_i\text{ for } i = 0, 1, \cdots , n − 2\), then the size of the receptive field of each element in $F_{i+1}$ is $(2^{i+2} − 1)×(2^{i+2} − 1)$.
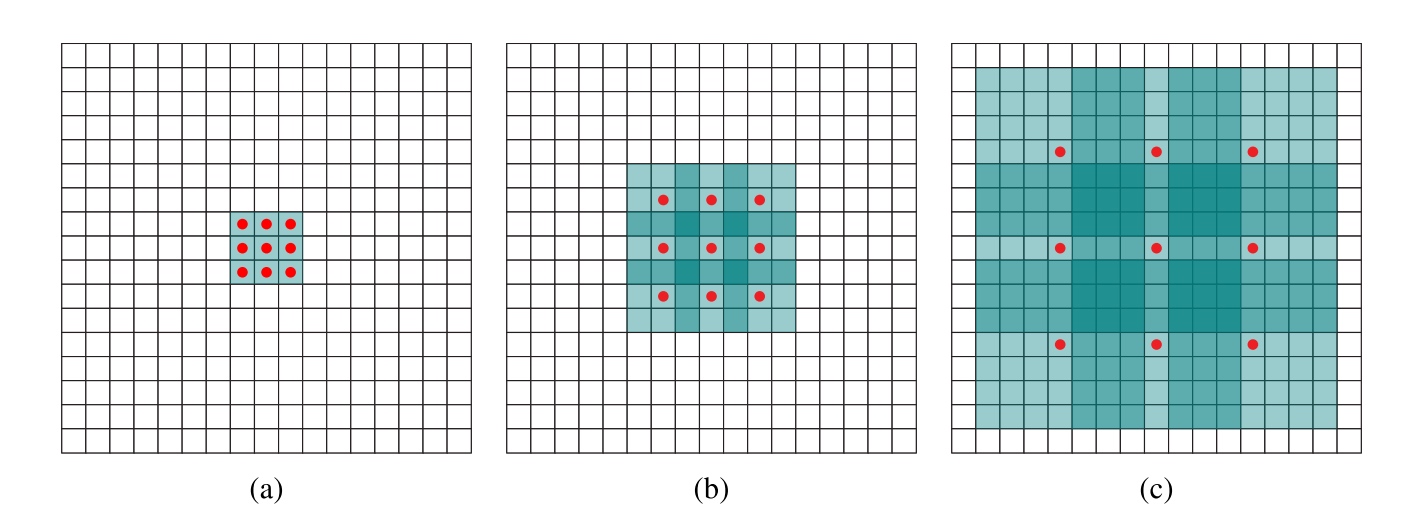
- $l$-dilated convolution: The familiar discrete convolution is simply the 1-dilated convolution.
- context module
The context module is designed to increase the performance of dense prediction architectures by aggregating multi-scale contextual information. The module takes C feature maps as input and produces C feature maps as output. The input and output have the same form, thus the module can be plugged into existing dense prediction architectures.
-
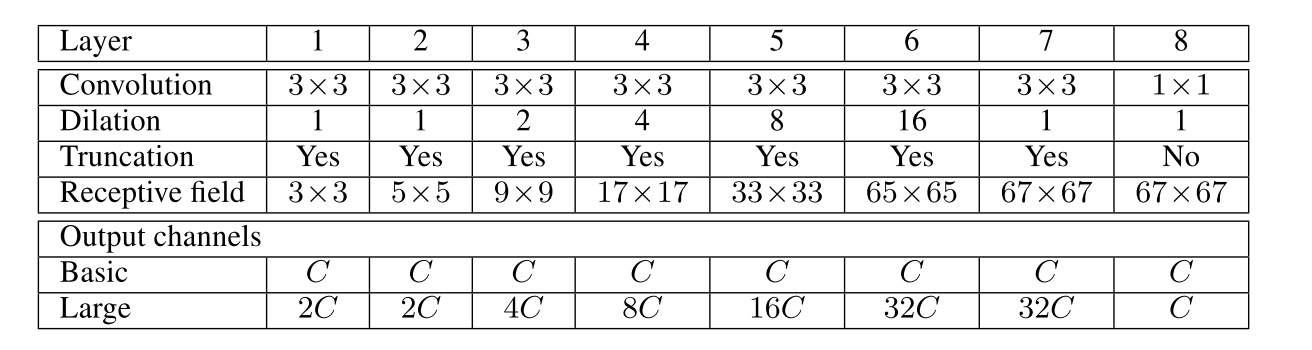
module architecture
here truncation is a ReLU function $f(\cdot)=max(\cdot, 0)$.
-
initialization
Experiments revealed that standard initialization procedures (random initialization) do not readily support the training of the module.
- Basic: identity initialization

- Large:

- Basic: identity initialization
-
- front end
- adapted the VGG-16 network for dense prediction and removed the last two pooling and striding layers. Specifically, each of these pooling and striding layers was removed and convolutions in all subsequent layers were dilated by a factor of 2 for each pooling layer that was ablated.
- use reflection padding: the buffer zone is filled by reflecting the image about each edge.
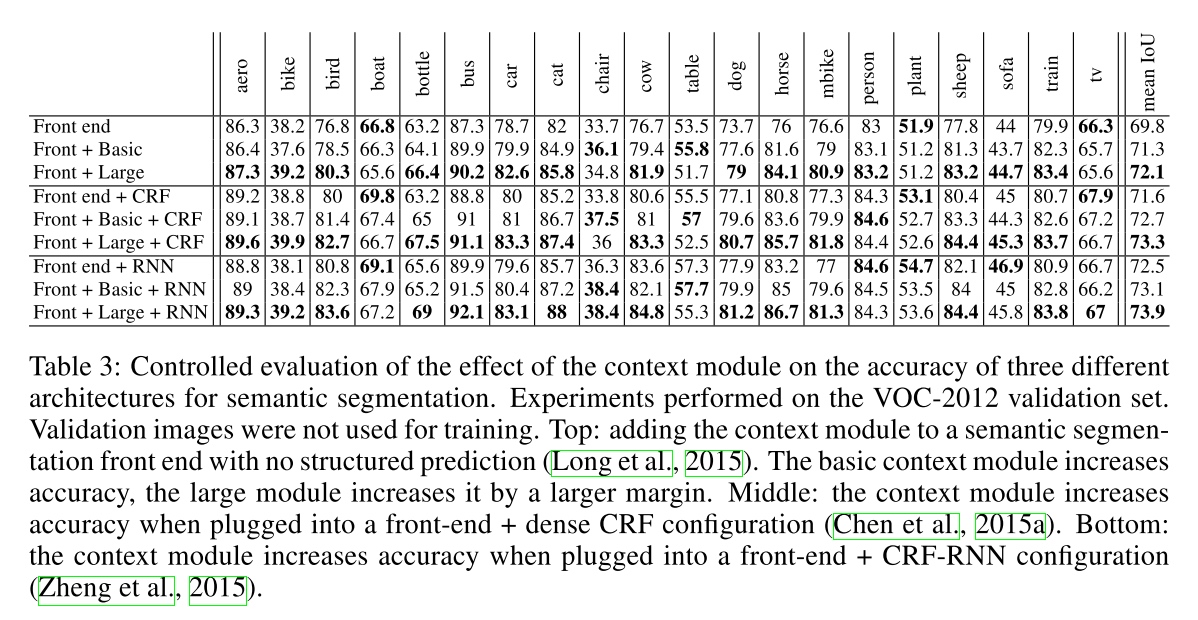
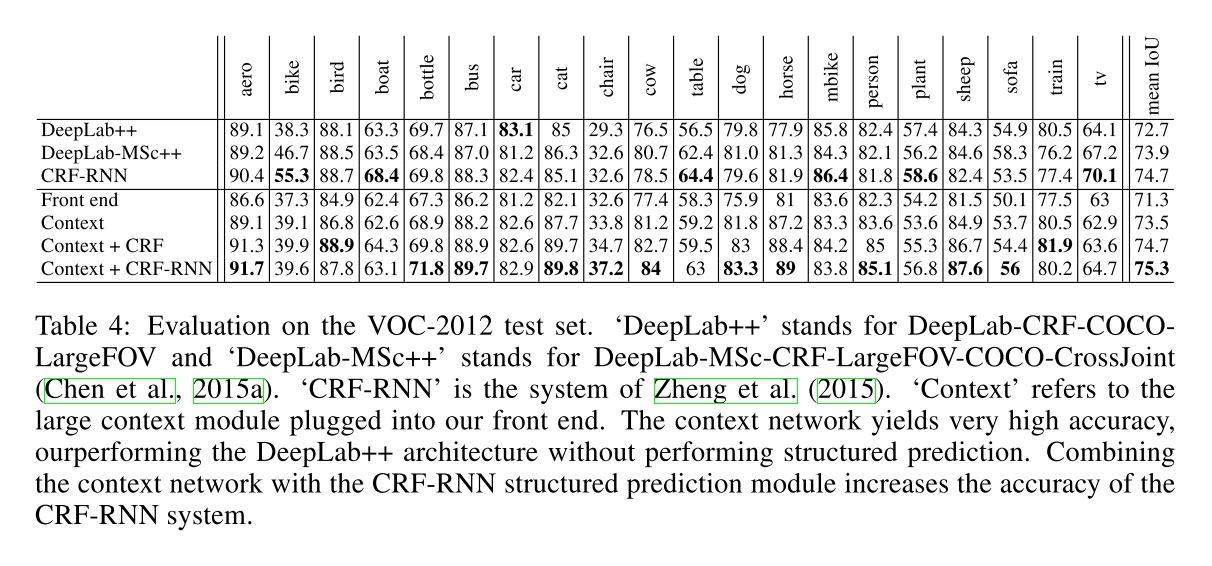
Result
-
Front end
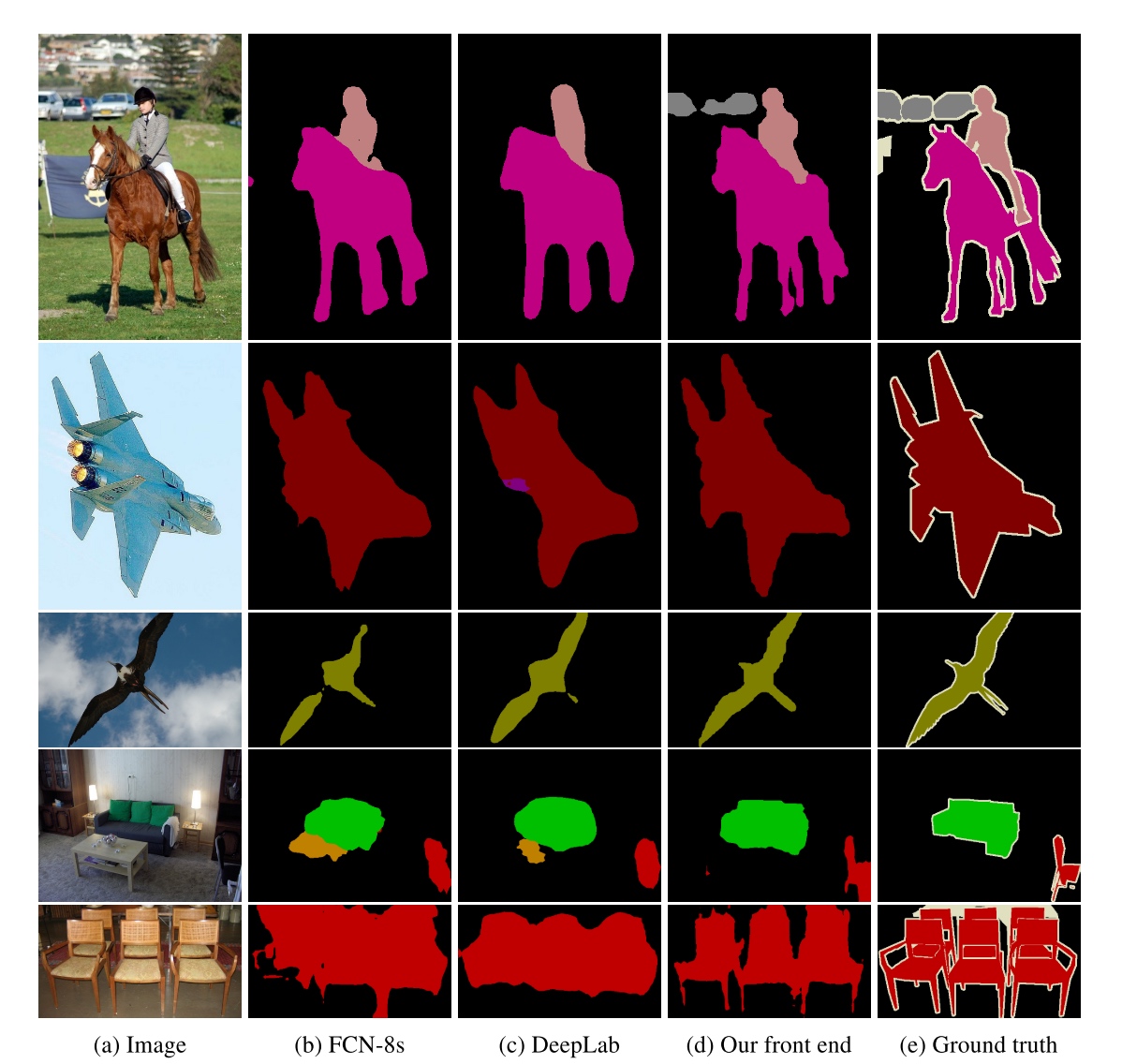

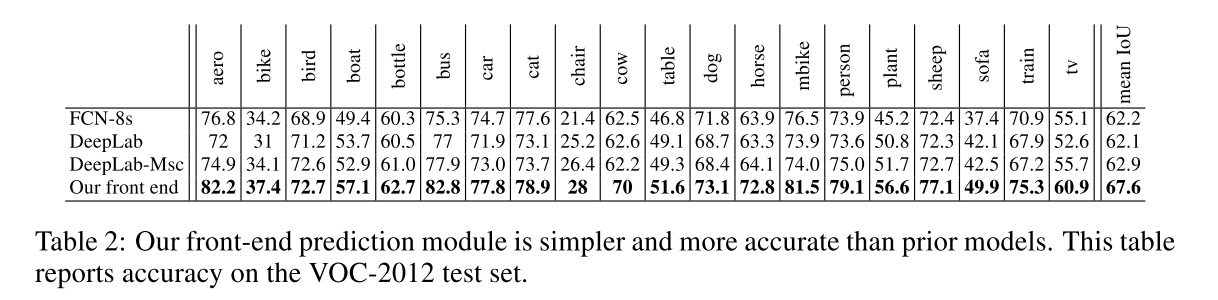
-
context module